Last Announcement of many funds under Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan by Finance Minister
Contents
- 1 Last Announcement of many funds under Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan by Finance Minister
- 1.1 Health Related Steps taken so far for COVID containment
- 1.2 Reforming Governance for Ease of Doing Business
- 1.3 Recent Corporate Law measures to boost Measures for Ease of Doing Business
- 1.4 Recent Corporate Law measures for Ease of Doing Business
- 1.5 Technology driven Systems – Online Education during COVID
- 1.6 Rs 40,000 crores increase in allocation for MGNREGS to provide employment boost
- 1.7 Health Reforms & Initiatives
- 1.8 Technology Driven Education with Equity post-COVID
- 1.9 Further enhancement of Ease of Doing business through IBC related measures
- 1.10 Decriminalisation of Companies Act defaults
- 1.11 Ease of Doing Business for Corporates
- 1.12 Public Sector Enterprise Policy for a New, Self-reliant India
- 1.13 Support already extended to State Governments
- 1.14 Supporting State Governments
- 1.15 Supporting State Governments & promoting state level reforms
- 1.16 Stimulus from earlier measures
Finance and Corporate Affairs Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitaraman has announced the 5th and last session of Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiya for Corporate sector, Education Sector and many sectors.
Health Related Steps taken so far for COVID containment
Already announced – Rs. 15,000 crore
• Released to states – Rs. 4113 cr
• Essential items – Rs. 3750 cr
• Testing labs and kits – Rs. 550 cr
• Insurance cover of Rs 50 lakhs per person for health professionals underPradhan Mantri GaribKalyan Yojana.
Leveraging IT –
• Roll out of e-Sanjeevani Tele-ConsultationServices
• Capacity Building: Virtual learning modules – iGOT platform
• Arogya Setu:self assessment and contact tracing
Protection to HealthWorkers –
• Amendment in Epidemic Diseases Act
• Adequate provision for PPEs –
• From zero to > 300 domestic manufacturers
• Already supplied – PPEs (51 lakhs), N95 masks (87 lakhs) HCQ tablets(11.08 Cr)
Reforming Governance for Ease of Doing Business
• Globally, potential investors look at a country’s Doing Business Report (DBR) ranking
• Sustained measures taken have resulted in steadily improving India’s position in World Bank’s Doing Business Report rank from 142 in 2014 to 63 in 2019
• This included streamlining processes such as granting of permits and clearance, self-certification and third party certification among others.
• Government is working on a mission mode on the next phase of Ease of Doing Business Reforms relating to easy registration of property, fast disposal of commercial disputes and simpler tax regime for making India one of the easiest places to do business
Recent Corporate Law measures to boost Measures for Ease of Doing Business
• In the first phase of decriminalization of Company Law defaults in 2018, 16 compoundable offences were shifted to an in-house adjudication & penalty mechanism
• Integrated Web based Incorporation Form – Simplified Proforma for Incorporating Company Electronically Plus (SPICe +) introduced which extends 10 services of different Ministries and one State Government through a single form.
• Databank of Independent Directors launched
• Withdrawal of more than 14,000 prosecutions under the Companies Act, 2013.
Recent Corporate Law measures for Ease of Doing Business
• Rationalization of Related Party Transaction related provisions
• Timely Action during COVID–19 to reduce compliance burden under various provisions of the Companies Act,2013 as well as enable Companies conduct Board Meetings, EGMs & AGMs, Rights issue by leveraging the strengths of Digital India
• In 221 resolved cases, 44% Recovery has been achieved since inception of IBC, 2016
• Admitted claims amount to Rs. 4.13 Lakh crores
• Realizable amount is Rs. 1.84 Lakh crores
• Under IBC, 13,566 cases involving a total amount of Rs. 5.01 lakh crores (approx.) have been withdrawn before admission under provisions of IBC till 29th Feb 2020.
Technology driven Systems – Online Education during COVID
• SWAYAM PRABHA DTH channels to support and reach those who do not have access to the internet. 3 channels were already earmarked for school education; now another 12 channels to be added.
• Provision made for telecast of live interactive sessions on these channels with experts from home through Skype.
• Also tied up with private DTH operators like Tata Sky & Airtel to air educational video content to enhance the reach of these channels.
• Coordination with States of India to share air time (4 hrs daily) on the SWAYAM PRABHA channels to telecast their education related contents.
• DIKSHA platform has had 61 crore hits from 24th March till date
• 200 new textbooks added to e-Paathshaala
Rs 40,000 crores increase in allocation for MGNREGS to provide employment boost
• Government will now allocate an additional Rs 40,000 crore under MGNREGS
• Will help generate nearly 300 crore person days in total
• Address need for more work including returning migrant workers in Monsoon season as well
• Creation of larger number of durable and livelihood assets including water conservation assets
• Will boost the rural economy through higher production.
Health Reforms & Initiatives
Increased investmentsin PublicHealth –
• PublicExpenditure on Health will be increased.
• Investmentsin grass root health institutions
• Ramp up Health and Wellness Centres in rural and urban areas
Preparing India for any future pandemics –
• Infectious Diseases HospitalBlocks – all districts
• Strengthening of lab network and surveillance –
o Integrated Public Health Labs in all districts & block level Labs & Public Health Unit to manage pandemics.
• Encouraging Research–National Institutional Platform for One health by ICMR
• National Digital Health Mission: Implementation of National Digital Health Blueprint
Technology Driven Education with Equity post-COVID
• PM eVIDYA- A programme for multi-mode access to digital/online education to be launched immediately; consisting of:
• DIKSHA for school education in states/UTs: e-content and QR coded Energized Textbooks for all grades (one nation, one digital platform)
• One earmarked TV channel per class from 1 to 12 (one class, one channel)
• Extensive use of Radio, Community radio and Podcasts
• Special e-content for visually and hearing impaired.
• Top 100 universities will be permitted to automatically start online courses by 30th May, 2020.
• Manodarpan– An initiative for psychosocial support of students, teachers and families for mental health and emotional wellbeing to be launched immediately.
• New National Curriculum and Pedagogical framework for school, early childhood and teachers will be launched: integrated with global and 21st century skill requirements
• National Foundational Literacy and Numeracy Mission for ensuring that every child attains Learning levels and outcomes in grade 5 by 2025 will be launched by December 2020
• Minimum threshold to initiate insolvency proceedings raised to Rs. 1 crore (from Rs. 1 lakh, which largely insulates MSMEs).
• Special insolvency resolution framework for MSMEs under Section 240A of the Code to be notified soon.
• Suspension of fresh initiation of insolvency proceedings up to one year depending upon the pandemic situation.
• Empowering Central Government to exclude COVID 19 related debt from the definition of “default” under the Code for the purpose of triggering insolvency proceedings.
Decriminalisation of Companies Act defaults
• Decriminalization of Companies Act violations involving minor technical and procedural defaults (shortcomings in CSR reporting, inadequacies in board report, filing defaults, delay in holding AGM).
• Majority of the compoundable offences sections to be shifted to internal adjudication mechanism (IAM) and powers of RD for compounding enhanced (58 sections to be dealt with under IAM as compared to 18 earlier).
• The Amendments will de-clog the criminal courts and NCLT
• 7 compoundable offences altogether dropped and 5 to be dealt with under alternative framework
Ease of Doing Business for Corporates
• Improvement in rankings in ‘starting a business’ and ‘insolvency resolution’ have contributed to the overall improvement in India’s ranking on EoDB.
• Further key reforms to include –
• Direct listing of securities by Indian public companies in permissible foreign jurisdictions.
• Private companies which list NCDs on stock exchanges not to be regarded as listed companies.
• Including the provisions of Part IXA (Producer Companies) of Companies Act, 1956 in Companies Act, 2013.
• Power to create additional/ specialized benchesfor NCLAT
• Lower penalties for all defaults for Small Companies, Oneperson Companies, Producer Companies & Start Ups.
Public Sector Enterprise Policy for a New, Self-reliant India
• India and the world have changed in the last few decades
• Need for a new coherent policy—where all sectors are open to the private sector while public sector enterprises(PSEs) will play an important role in defined areas
• Accordingly government will announce a new policy whereby
• List of strategic sectors requiring presence of PSEs in public interest will be notified
• In strategic sectors, at least one enterprise will remain in the public sector but private sector will also be allowed
• In othersectors, PSEs will be privatized (timing to be based on feasibility etc.)
• To minimize wasteful administrative costs, number of enterprises in strategic sectors will ordinarily be only one to four; others will be privatized/ merged/ brought under holding companies
Support already extended to State Governments
• Centre, like the states, has faced a sharp decline in revenues
• Despite this the Centre has consistently extended generous support to states in this hour of need
• Devolution of taxes (Rs 46,038 cr) in April was given fully as if Budget Estimates were valid, even though actual revenue shows unprecedented decline from Budget Estimates
• Revenue Deficit Grants to states (Rs 12,390 cr) given on time in April and May, despite Centre’s stressed resources
• Advance release of SDRF (Rs. 11,092 cr) funds in first week of April
• Release of over Rs. 4,113 crores from Health Ministry for direct anti-Covid activities
• At Centre’s request, RBI has increased
• Ways & Means Advance limits of States by 60%
• Number of days state can be in continuous overdraft from 14 days to 21 days
• Number of days state can be in overdraft in a quarter from 32 to 50 days.
Supporting State Governments
• States net borrowing ceiling for 2020-21 is Rs. 6.41 lakh crores, based on 3% of Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP)
• 75% thereof was authorised to them in March 2020 itself and timing is left to the States
• States have so far borrowed only 14% of the limit authorised. 86% of the authorised borrowing remains unutilized.
• Nevertheless, states have been asking for special increase in borrowing from 3% to 5%
• In view of the unprecedented situation, Centre has decided to accede to the request and increase borrowing limits of States from 3% to 5%, for 2020-21 only.
• This will give States extra resources of Rs. 4.28 lakh crores
Supporting State Governments & promoting state level reforms
• Part of the borrowing will be linked to specific reforms (including recommendations of Finance Commission) to:
• ensure sustainability of the additional debt through higher future GSDP growth and lower deficits;
• promote welfare of migrants and reduce leakage in food distribution,
• increase job creation through investment
• safeguard the interests of farmers while making the powersectorsustainable, and
• promote urban development, health and sanitation
• Reform linkage will be in four areas: universalisation of ‘One Nation One Ration card’, Ease of Doing Business, Power distribution and Urban local body revenues
• A specific scheme will be notified by Department of Expenditureon the following pattern:
• Unconditionalincreaseof 0.50%
• 1% in 4 tranches of 0.25%, with each tranche linked to clearly specified, measurable and feasible reform actions
• Further 0.50%if milestones are achieved in at leastthree out of four reform areas
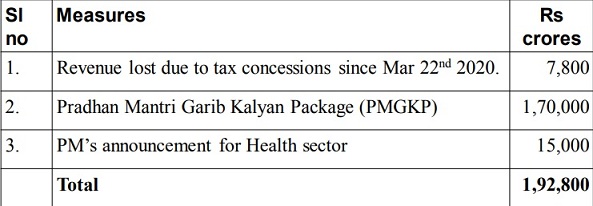
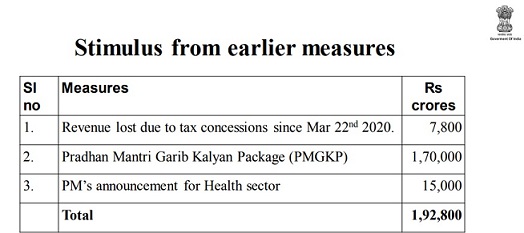
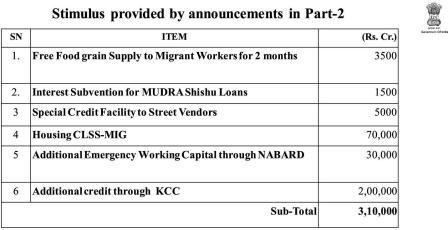
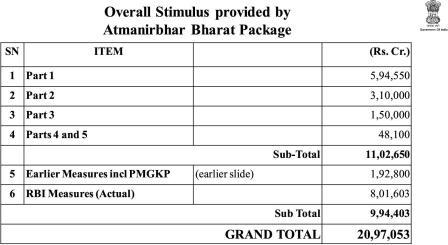
Stimulus from earlier measures
For details of this Announcement: Direct Link
Source: PIB